Choosing the right construction components is crucial for creating a home that is both comfortable and low-cost to run. The use of sustainable building materials for energy efficiency is no longer a niche trend but a smart investment in our planet and our wallets. These materials are designed to minimize heat loss and gain, directly reducing reliance on heating and cooling systems and lowering your home’s overall carbon footprint.
Contents
What defines sustainable and energy efficient materials
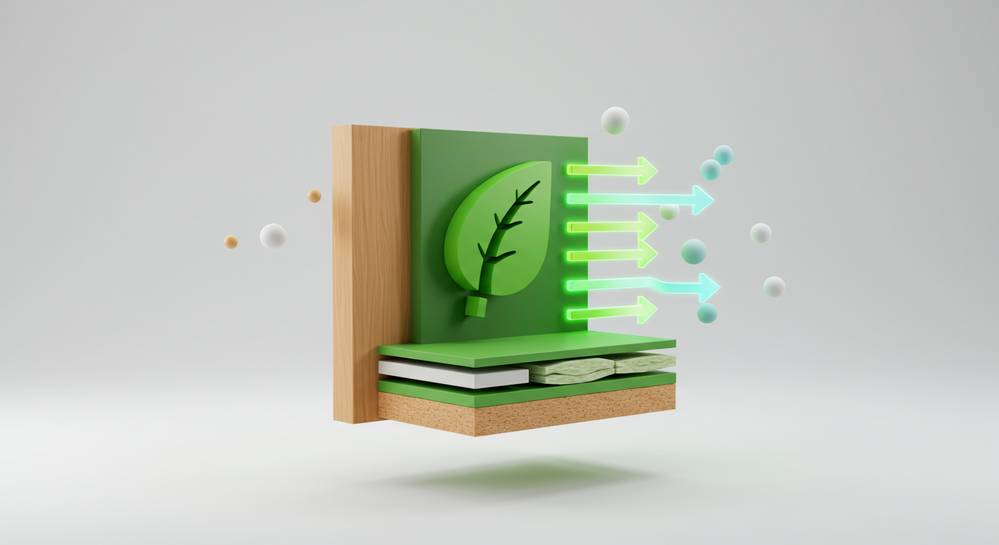

To understand what makes a building material both sustainable and energy efficient, we must look beyond its initial cost. The criteria involve its entire lifecycle, from production to disposal. Truly effective sustainable building materials for energy efficiency excel at reducing a building’s energy needs while minimizing environmental harm. This dual focus is the cornerstone of modern green construction and a wise long term investment.
Key characteristics to consider
- Low Embodied Carbon: This refers to the total greenhouse gas emissions from a material’s extraction, manufacturing, and transportation. Materials like locally sourced timber or bamboo have significantly lower embodied carbon than concrete or steel.
- High Thermal Resistance (R-value): A high R-value indicates better insulation. Materials like cork or sheep wool are excellent at preventing heat transfer, meaning your heating and cooling systems work less, saving energy.
- Recycled and Reclaimed Content: Using materials such as recycled steel or insulation made from reclaimed paper reduces landfill waste. It also cuts the energy required to produce new materials from scratch.
- Durability and Longevity: Materials that last longer require fewer replacements, reducing the long term environmental impact. Slate roofing or durable hardwoods are prime examples of this principle.
Choosing materials based on these factors ensures your building is not only cheaper to run but also contributes positively to the environment. It is a strategic investment in both financial savings and ecological responsibility.
Top sustainable materials for thermal insulation
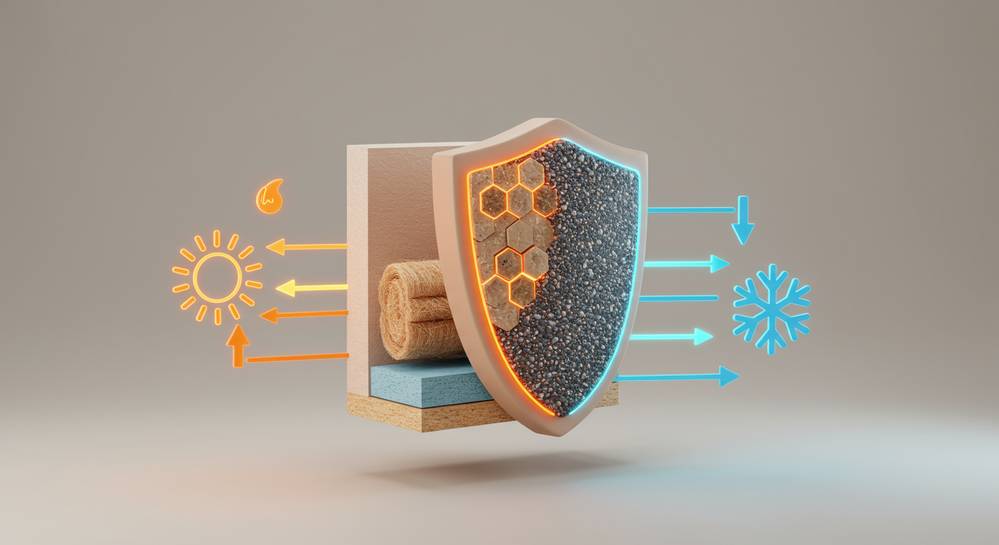
Effective insulation is the first line of defense against energy loss in any building. It works by slowing the transfer of heat, keeping your home warm in the winter and cool in the summer. Sustainable insulation materials achieve this without the environmental baggage of traditional options like fiberglass. They are often non-toxic, biodegradable, and sourced from renewable resources, making them excellent sustainable building materials for energy efficiency.
Leading sustainable insulation choices
- Cork: Harvested from the bark of cork oak trees without harming the tree, cork is a fantastic insulator. It is moisture-resistant, fire-retardant, and provides excellent acoustic insulation. Its honeycomb structure traps air, making it highly effective at maintaining stable indoor temperatures.
- Sheep Wool: A natural and renewable fiber, sheep wool is an exceptional insulator. It can absorb and release moisture without compromising its thermal performance, helping to regulate humidity. It is also naturally flame-resistant and helps to improve indoor air quality by trapping harmful compounds.
- Cellulose Insulation: Made from recycled paper products, cellulose is a low-cost and highly effective option. It is treated with non-toxic borates to resist fire, pests, and mold. Blown-in cellulose fills wall cavities completely, creating a tight seal that significantly reduces air leakage.
- HempCrete: A mixture of hemp hurds and lime, HempCrete is a lightweight, breathable material that provides both insulation and thermal mass. It is carbon-negative, meaning it absorbs more CO2 during its life than is emitted during its production.
Structural materials that enhance energy performance
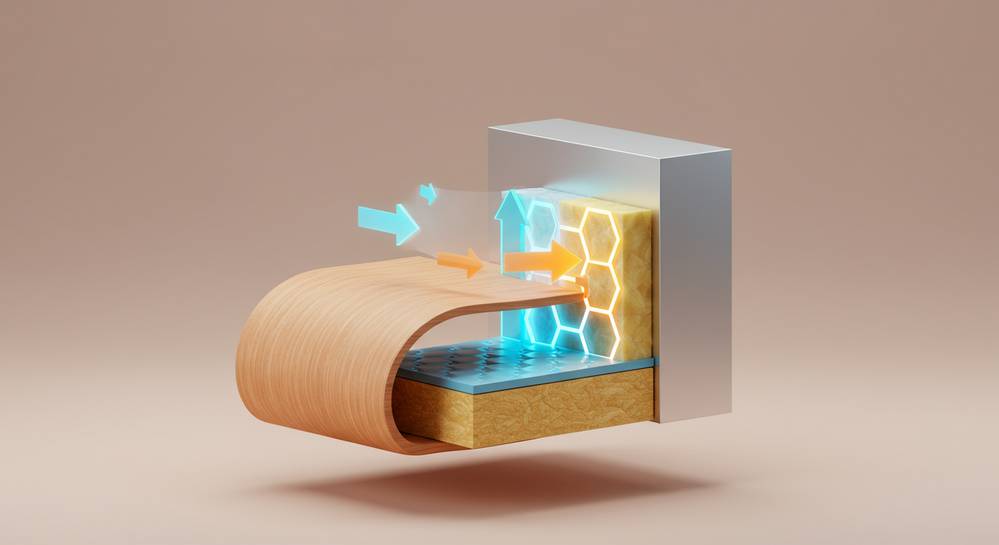
A building’s structural frame is its skeleton, and choosing the right materials here has a massive impact on its overall energy performance. Sustainable structural materials are not only strong and durable but also possess inherent properties that contribute to a more energy efficient building envelope. This approach moves beyond just insulation, focusing on the core strength and sustainability of the entire structure.
Eco-friendly structural innovations
- Cross-Laminated Timber (CLT): CLT panels are made by gluing layers of solid lumber together. This process creates exceptionally strong and stable panels for walls, floors, and roofs. Timber is a renewable resource that sequesters carbon, and CLT construction is fast and efficient, a key principle when you learn how to build a smart home.
- Bamboo: Technically a grass, bamboo grows incredibly fast and has a tensile strength comparable to steel. It is a highly renewable resource ideal for framing and flooring. Laminated bamboo lumber offers a strong and sustainable alternative to traditional hardwoods.
- Recycled Steel: While steel production is energy intensive, using recycled steel drastically reduces its environmental impact. It requires up to 75% less energy than producing it from raw materials. Steel framing is durable, lightweight, and pest resistant.
- Reclaimed Wood: Sourced from old buildings and barns, reclaimed wood adds character to a project. It prevents old growth timber from going to a landfill and reduces the demand for new logging.
How to choose the right materials for your project
Selecting the ideal sustainable building materials for energy efficiency requires a balanced approach. You must consider your projects unique context. What works for a cold climate might be unsuitable for a hot, arid region. A thoughtful selection process ensures you maximize both energy efficiency and long term value for your specific needs.
Factors to guide your decision
- Climate and Location: Your local climate is the most critical factor. In colder regions, prioritize materials with high R-values for insulation. In hot climates, focus on materials with high thermal mass. Sourcing locally also reduces transportation emissions.
- Budget and Lifecycle Cost: While some materials have a higher upfront cost, consider the lifecycle cost. Superior insulation and durable materials lead to significant long term savings on energy bills and maintenance, offering a strong return on investment.
- Building Codes and Regulations: Always check with your local building authority. Ensure the materials you are considering comply with regional codes. Some innovative materials may require specific permits or engineering approvals.
- Aesthetic and Design Goals: Your desired look and feel will also influence your choices. Reclaimed wood offers a rustic aesthetic, while bamboo can create a modern vibe. Ensure your material choices align with your overall architectural vision.
Embracing sustainable building materials is a practical and powerful step toward creating a home that is both energy-efficient and environmentally responsible. By prioritizing materials with low embodied carbon, high insulation values, and longevity, you invest in a future of lower energy bills and a healthier planet. For more insights on smart home technology and sustainable living, explore Home Gadget Digest.















+ There are no comments
Add yours